Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ishino, Masahiko; Faenov, A.*; Tanaka, Momoko; Hasegawa, Noboru; Nishikino, Masaharu; Tamotsu, Satoshi*; Pikuz, S.*; Inogamov, N. A.*; Zhakhovsky, V. V.*; Skobelev, I.*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1465, p.236 - 240, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:62.21(Physics, Applied)We irradiated the focusing soft X-ray laser pulses having a wavelength of 13.9 nm and the duration of 7 ps to aluminum surface. After the irradiation process, the irradiated surface was observed with a scanning electron microscope. The surface modifications caused by soft X-ray laser single pulse exposure were clearly seen. In addition, it was found that the conical structures having around 100 nm in diameters were formed in the shallow features. The nano-meter size modified surface structures on aluminum induced by the soft X-ray laser pulse is interesting as the newly surface structure. Hence, the soft X-ray laser beam would be a candidate for a tool of micromachining. We also provide a thermomechanical modeling of the soft X-ray laser interaction with aluminum briefly to explain the surface modification.
Yokoyama, Keiichi
AIP Conference Proceedings 1465, p.65 - 68, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)Design of experiments to demonstrate the isotope-selective displacement of rotational state distribution is reported for future demonstration using realistic terahertz pulse train. Elements to be designed include species used as a target and methods to prepare the target, to prepare THz pulse train, and to measure the distribution. As a result, lithium chloride has been chosen as the target molecule, which is prepared as He-seeded supersonic molecular beam produced with a high-temperature CW nozzle. The terahertz pulse train is prepared by a three-stage interferometer or etalon. The rotational state distribution is measured by momentum imaging spectroscopy. Numerical simulation of the selective displacement is carried out under the chosen condition.
Imazono, Takashi; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; Sasai, Hiroyuki*; Oue, Yuki*; Yonezawa, Zeno*; Kuramoto, Satoshi*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1465, p.33 - 37, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:83.30(Physics, Applied)Imazono, Takashi; Sano, Kazuo*; Koike, Masato
AIP Conference Proceedings 1465, p.28 - 32, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:45.36(Physics, Applied)Imazono, Takashi; Moriya, Naoji*; Harada, Yoshihisa*; Sano, Kazuo*; Koike, Masato
AIP Conference Proceedings 1465, p.38 - 42, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)Hasegawa, Noboru; Yamamoto, Minoru*; Terakawa, Kota*; Nishikino, Masaharu; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Minami, Yasuo*; Tomita, Takuro*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Suemoto, Toru
AIP Conference Proceedings 1465, p.23 - 27, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)We have developed a soft X-ray laser (SXRL) interferometer capable of the single-shot imaging of nano-scaled structure dynamics. The depth and lateral resolutions of the interferometer were about 1 nm and 1.8 micron, respectively. We observed the initial stage ( 50 ps) of the ablation process of the Pt surface pumped by a 70 fs Ti:Sapphire laser pulse. The expansion speed of the Pt surface (34 nm/50 ps) indicated that the nano-bubble structures were formed in the initial stage of the ablation. In order to observe the detailed dynamics, the precision of temporal synchronization between the pump and probe pulses was improved to be 3 ps by adopting a portion of the SXRL and pump beams as the time fiducials.
50 ps) of the ablation process of the Pt surface pumped by a 70 fs Ti:Sapphire laser pulse. The expansion speed of the Pt surface (34 nm/50 ps) indicated that the nano-bubble structures were formed in the initial stage of the ablation. In order to observe the detailed dynamics, the precision of temporal synchronization between the pump and probe pulses was improved to be 3 ps by adopting a portion of the SXRL and pump beams as the time fiducials.
Koike, Masato; Imazono, Takashi
AIP Conference Proceedings 1465, p.202 - 206, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)Soft X-ray multilayer has a potential to improve diffraction efficiency of diffraction gratings in the multi-kilo electron volts region. However, to use a conventional multilayer grating at the maximum diffraction efficiency, the incidence and diffraction angles should be varied with photon energy. Recently we developed a wide-band laminar-type multilayer grating for the flat-field spectrograph used in the energy range of 2-4 keV. The structure of the multilayer consists of two regions of massive and few periods having short and long period lengths, respectively, to widen the bandwidth. This method worked successfully that a diffraction efficiency of 1-2 % was obtained experimentally. Another interest on this method is the application to the monochromators. In this paper, we design the diffraction efficiency of the multilayer laminar-type grating covering 1.5-2.5 keV and estimate the throughput of a Monk-Gillieson type monochromator employing this grating.
Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Ogaki, Hideaki; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Komatsubara, Tetsuro*
no journal, ,
Nuclear electromagnetic (EM) transitions can be studied by nuclear photon scattering, or nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF). Recently, it was shown that a quasi-monochromatic, linearly polarized photon beam produced by inverse Compton scattering increased experimental sensitivities to distinguish between electric and magnetic dipole transitions. Here we report the results of the nuclear photon scattering measurements on  Fe using a quasi-monochromatic, linearly polarized photon beam derived at National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Tsukuba. Many dipole resonances below the neutron separation energy of
Fe using a quasi-monochromatic, linearly polarized photon beam derived at National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Tsukuba. Many dipole resonances below the neutron separation energy of  Fe (11.2 MeV) have been observed. The multi-polarities of these transitions were determined by intensity asymmetry relative to the polarization of the incident photon beam. The experimental results are compared with a shell model calculation.
Fe (11.2 MeV) have been observed. The multi-polarities of these transitions were determined by intensity asymmetry relative to the polarization of the incident photon beam. The experimental results are compared with a shell model calculation.
Terauchi, Masami*; Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Handa, Nobuo*; Murano, Takanori*; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Imazono, Takashi; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; et al.
no journal, ,
Soft X-ray emission spectroscopy (SXES) combined with electron microscopy should be a hopeful method to reveal physical properties and chemical-bonding states of identified small specimen areas of various compounds. A new SXES development for electron microscopes (TEM and electron-probe microanalyzer) has started to obtain an energy range from 50 eV to 4000 eV by using four aberration-corrected (varied-line-spaced: VLS) gratings. An extension in lower energy region was achieved by a design and manufacturing a new VLS grating with a groove density of 1200 l/mm at a grazing incident angle of 4 deg. This grating enables us to detect Li-K emission (54 eV) with an energy resolution of 0.3 eV. A new multilayer-coated (MLC) VLS grating with a groove density of 2400 l/mm has designed and manufactured for obtaining SXES spectra up to 4 keV at a grazing incident angle of 1.35 deg. The material pair of the multilayer is W and B C. This new MLC-VLS grating can measure not only Te-L
C. This new MLC-VLS grating can measure not only Te-L (3769eV) and L
(3769eV) and L (4030 eV) but also four small structures of Ll, L
(4030 eV) but also four small structures of Ll, L , L
, L
 and L
and L
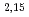 . At the same setting, Al-K
. At the same setting, Al-K (1486 eV), Pt-M
(1486 eV), Pt-M (2050 eV), Pd-M
(2050 eV), Pd-M (2839 eV), In-L
(2839 eV), In-L (3287 eV) were also observed. This confirms that this newly designed MCL grating works for 1.5-4 keV.
(3287 eV) were also observed. This confirms that this newly designed MCL grating works for 1.5-4 keV.